Table of contents
Sales compensation plays a crucial role in motivating and retaining top-performing sales representatives. Among the many elements of sales incentives, the concept of the “average sales commission” stands out as a key metric for businesses looking to optimize their compensation strategies. Whether you are designing a commission-based plan or analyzing how your sales teams stack up against industry benchmarks, understanding average sales commission is essential for aligning business goals with sales performance.
This guide explores the factors influencing average sales commission, the types of structures available, and real-world examples to illustrate their impact. Let’s take a look!
What is average sales commission?
Average sales commission refers to the percentage or amount that a company pays sales representatives as a reward for closing deals or meeting sales quotas. This metric is commonly calculated by dividing the total commissions paid to sales teams by the total sales they generate. Businesses often use this value to benchmark their compensation plans against industry standards and ensure their strategies align with long-term business goals.
Why does it matter?
The right sales commission rate motivates sales representatives to exceed their quotas and ensures that businesses achieve their revenue targets. Striking a balance is vital: offering a commission too low can lead to disengaged teams, while excessively high rates may eat into profit margins. By analyzing average sales commission, organizations can maintain competitive pay structures, retain talent, and drive consistent sales performance.
Common factors influencing average sales commission
1. Industry standards:
Commission rates vary significantly by industry. For example, SaaS companies may offer commissions between 5% and 10%, while real estate sales representatives often see higher commission rates closer to 3% of the total amount of the sale.
2. Products or services sold:
High-ticket items like luxury cars or enterprise software may involve lower percentages but generate significant earnings for sales reps. Conversely, consumable products or lower-cost items may use higher percentages to incentivize volume-based sales.
3. Sales roles and responsibilities:
Entry-level sales representatives typically receive a lower base salary plus commission, while senior roles with larger territories often receive higher commission rates, residual commission opportunities, or territory volume commission structures.
4. Sales quotas and targets:
Businesses often adjust commission rates based on whether sales reps meet or exceed quotas. For instance, a company might offer 5% for meeting a quota but escalate to 8% for surpassing it by 20%.
5. Compensation structure:
There are various types of sales commission structures, including commission-only models, base pay plus commission, and tiered commissions. Each structure affects the average sales commission differently.
Types of sales commission structures and their impact
1. Commission only
Sales reps earn no base salary and rely entirely on commissions. While the average sales commission rates in this model are high (often 20% or more), the lack of guaranteed pay may not suit all sales roles.
2. Base salary plus commission
This is the most common structure, offering a base rate with additional earnings tied to performance. For example, a sales representative in the healthcare industry might earn a base pay of $50,000 annually, with a 10% commission on sales over $500,000.
3. Tiered commission structures
In this model, rates increase as sales reps hit milestones. For example:
- 5% commission for sales up to $100,000
- 7% commission for sales between $100,001 and $200,000
- 10% commission for sales exceeding $200,000
This structure rewards high performers and drives long-term sales growth.
4. Residual commission
Sales representatives continue to earn a commission on ongoing contracts or renewals. This is common in subscription-based services or insurance and often results in higher commission rates over time.
5. Territory volume commission:
Businesses assign specific territories to sales reps, and commissions are based on the total amount of sales within that territory. For example, a sales rep might earn 6% of the total volume generated in their region.

Real-world examples
- Technology sector:
A SaaS company employs a base salary plus commission structure. Sales reps receive $60,000 annually, with a 7% commission on all sales over $1 million. The average sales commission for top performers in this company is $30,000 annually, making their total OTE $90,000. - Real estate:
Sales representatives earn 3% of the sale price of properties. If a sales rep sells $10 million worth of homes annually, their average sales commission amounts to $300,000. While the percentage is relatively low, the high ticket value ensures substantial earnings. - Retail:
A clothing brand uses a tiered commission structure for sales associates. Employees earn:- 2% for monthly sales up to $10,000
- 4% for sales between $10,001 and $20,000
- 6% for sales over $20,000
For an associate achieving $25,000 in monthly sales, the average sales commission totals $1,200.
Benchmarking average sales commission by industry
Benchmarking helps companies understand whether their sales incentives align with market standards. Here are examples of average sales commission rates by industry:
- Insurance: 8%-12% of premium value
- Automotive: 20%-25% of gross profit
- B2B SaaS: 5%-10% of total contract value
- Manufacturing: 3%-7% of sales value
- Retail: 1%-6% of revenue
These benchmarks demonstrate how commission rates differ based on products or services and sales roles. Businesses can use these insights to fine-tune their strategies and improve sales performance.
How to calculate average sales commission
To calculate average sales commission, follow these steps:
- Determine the total commissions paid over a specific period.
- Calculate the total sales revenue for the same period.
- Divide the total commissions by total sales and multiply by 100 to get the percentage.
For example:
-
-
- Total sales revenue: $1,000,000
- Total commissions paid: $100,000
-
-
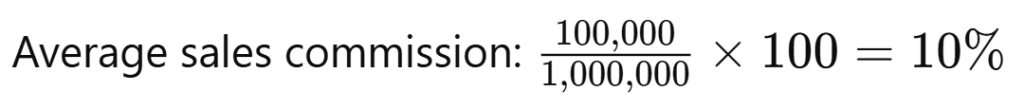
Aligning commissions with business success
Understanding average sales commission is critical for designing effective sales incentives that align with business goals and drive better performance. By considering factors such as industry benchmarks, compensation structures, and the nature of products or services, businesses can optimize their strategies to retain top talent, meet quotas, and achieve sustainable growth. Whether your company uses residual commissions, tiered structures, or territory-based systems, keeping average sales commission rates competitive ensures your sales teams remain motivated and productive.
At Remuner, we make managing and optimizing sales commission plans effortless. Our platform automates all aspects of compensation, connects seamlessly with your existing systems, and provides real-time dashboards to keep your teams aligned and motivated. With features like a no-code plan designer and an AI-based sales coach, you can create data-driven compensation strategies that drive exceptional sales performance. Discover how Remuner can transform your compensation plans today.